What is a Renal Ultrasound?
Renal ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging method that uses ultrasound waves to obtain images of your kidneys.
These images can help your doctor assess the position, size, and shape of your kidneys, as well as the blood flow to your kidneys. Kidney ultrasound is often evaluated together with the bladder as a urinary system ultrasound.
Ultrasound or sonography uses high-frequency sound waves sent by a probe pressed against your skin. The sound waves travel through your body, bounce off organs, and return to the probe. The returning sound waves are recorded and transformed into images or videos of selected tissues and organs for digital examination.
Ultrasound is not dangerous and has no known harmful side effects. Unlike X-ray examinations, ultrasound does not use radiation.
How do the kidneys work?
The body takes in nutrients and converts them into energy. After the body digests the nutrients it needs, the waste products remain in the intestines and blood.
The kidneys and urinary system balance minerals like potassium and sodium and remove wastes such as urea from the blood. Urea is produced when foods containing protein, such as meat, poultry, and some vegetables, are broken down in the body. Urea is transported to the kidneys through the bloodstream. The kidneys also produce a hormone called erythropoietin, which helps in the formation of red blood cells, and they regulate blood pressure.
When is a renal ultrasound performed?
Your doctor may request a renal ultrasound if they think you have a problem with your kidneys and need more information.
The main conditions that can be detected by a renal ultrasound include kidney abscess, urinary tract obstruction, kidney cysts, infection, kidney stones, kidney tumors.
Other reasons you might need a kidney ultrasound include:
Guidance for a needle biopsy of the kidney, aspiration of fluid from a kidney abscess or cyst.
Guidance for placing a drainage tube into the kidney.
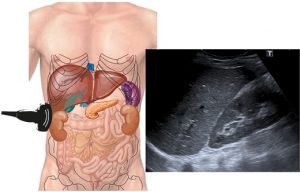
Routine images consist of long-axis and transverse views. The normal kidney length is approximately 11 to 12 cm. Normal width is about 4 to 5 cm. The renal cortex should be evaluated in terms of echogenicity, contour, and thickness.
The normal renal cortex is isoechoic or hypoechoic compared to the liver and spleen. Sometimes a hump-like projection in the midsection of the left kidney may be seen in the cortex. This occurs due to pressure from the spleen on the left kidney and displays normal parenchymal features.
Kidneys should be evaluated for atrophy, scar tissue, calcification, hydronephrosis, and masses.
The renal medulla contains pyramids that are hypoechoic compared to the cortex. The renal sinus is more centrally located and appears echogenic due to fatty tissue. The renal sinus includes the main branches of the renal artery and vein, the collecting system, and lymphatics.
When hydronephrosis is present, the affected collecting system should always be compared with the opposite side. This provides information about whether hydronephrosis is unilateral or bilateral, and the level and location of obstruction. In cases of hydronephrosis, the size of the kidney can be compared with previous studies, if available.
The detection of kidney stones via ultrasound depends on factors such as the size and location of the stone, the primary factors being the composition of the stone, hydration status, hydronephrosis, and the presence of kidney or vascular disease.
One of the most common abnormalities in the kidneys is cysts. Cysts are generally asymptomatic. Uncomplicated cysts have thin walls, anechoic content, and enhanced sound transmission.
The size of cysts can vary significantly. It is important to carefully assess the cyst wall and rule out any solid components. If solid components or septations are present, additional characterization using abdominal CT is indicated.
One of the most common malignant lesions in the kidney is renal cell carcinoma (RCC). It is typically a solid mass with a heterogeneous echo pattern and vascularization.
Renal Ultrasound Prices 2026
Renal ultrasound prices vary from region to region and even from institution to institution in the same region. For information on renal ultrasound prices, you can call 02126321059.

