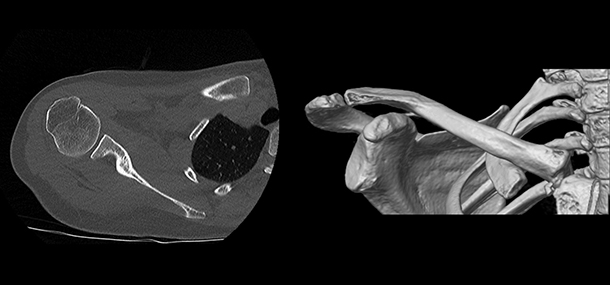
Computed tomography (CT) is a radiological examination that, like traditional X-rays, produces numerous images or pictures of the inside of the body.
The cross-sectional images produced during a CT scan can be reformatted in multiple planes and even create three-dimensional images. These images can be viewed on a computer monitor, printed on film, or transferred to a CD or DVD.
CT images of internal organs, bones, soft tissue, and blood vessels provide more detailed information than conventional soft beam X-rays, particularly for soft tissues and blood vessels.
Radiologists who use specialized equipment and expertise to create and interpret CT scans of the body can diagnose problems such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, infectious diseases, appendicitis, trauma, and musculoskeletal disorders more easily.
What Are the Common Uses of Computed Tomography?
- One of the fastest and most accurate examinations for evaluating the chest, abdomen, and pelvis because it provides detailed cross-sectional images of every tissue type.
- It is used to examine patients who are injured due to trauma, such as in a motor vehicle accident.
- It is performed on patients with acute symptoms such as chest or abdominal pain or breathing difficulty.
- It is often the best method for detecting cancers, such as lung, liver, kidney, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers. It is considered the best method as it allows the doctor to confirm the presence of a tumor, measure its size, define its exact location, and determine its relationship with nearby tissues.
- It plays an essential role in detecting, diagnosing, and treating vascular diseases that can lead to stroke, kidney failure, and even death. CT scanning is widely used to evaluate pulmonary embolism (a blood clot in the lung vessels) and aortic aneurysms.
CT Scanning in Pediatric Patients:
- Lymphoma
- Neuroblastoma
- Kidney tumors
- Congenital malformations of the heart, kidneys, and blood vessels
- Cystic fibrosis
- Complications of acute appendicitis
- Complications of pneumonia
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Severe injuries
Radiologists and radiation oncologists frequently use CT scans to:
- Quickly identify injuries to the lungs, heart and vessels, liver, spleen, kidneys, intestines, or other internal organs in trauma cases.
- Guide other procedures such as biopsies, abscess drainages, and minimally invasive tumor treatments.
- Plan and assess surgical outcomes for procedures like organ transplants or gastric bypass surgery.
- Monitor response to chemotherapy and stage and plan radiation treatments for tumors.
How Should I Prepare for a Computed Tomography (CT) Scan?
Metal objects, including jewelry, eyeglasses, dentures, and hairpins, can affect CT images and should be left at home or removed before the exam. Women will be asked to remove bras containing metal. If possible, you may be asked to remove piercings.
If a contrast material is used for the CT scan, you will be asked to refrain from eating or drinking for a few hours beforehand. You should inform your doctor of all medications and allergies. If you are allergic to the contrast material, your doctor may prescribe medications to reduce the risk of an allergic reaction.
You should also inform your doctor about recent illnesses, other medical conditions, and a history of heart disease, asthma, diabetes, kidney disease, or thyroid problems. Women should always notify their doctors and CT technicians if there is a possibility they are pregnant.
How Is a CT Scan Performed?
In many ways, a CT scan works similarly to other X-ray exams. During a CT scan, numerous X-ray beams and a set of electronic X-ray detectors rotate around you, measuring the amount of radiation absorbed by your body. Sometimes, the examination table moves during the scan so that the X-ray beam follows a spiral path. When the image slices are reconstructed by computer software, the result is a highly detailed, multidimensional view of the body’s interior.
Advancements in detector technology allow almost all CT scanners to obtain multiple slices in a single rotation. These scanners, called multidetector or multislice CT, enable the acquisition of thinner slices in a shorter amount of time, resulting in more detailed and additional images.
Modern CT scanners are so fast that they can scan large sections of the body in just a few seconds, and even faster in smaller children. This speed benefits all patients, especially children, the elderly, and critically ill patients who may struggle to remain still even for the short period required to obtain images.
For children, the CT scanner technique is adjusted based on their size and area of interest to reduce radiation exposure. Some CT scans use contrast material to enhance visibility in the area of the body being examined. You may be asked to hold your breath during the scan, as breathing or body movements can blur the images.
CT scans are typically painless, fast, and easy. With multidetector CT, the amount of time the patient needs to lie still is significantly reduced.
Except for special circumstances, you will be alone in the exam room during the CT scan. Sometimes a parent wearing a lead apron may stay in the room with children. However, the technician can talk to you and hear you through an intercom system.
For pediatric patients, a parent may enter the room, but they must wear a lead apron to minimize radiation exposure.
After a CT scan, you can return to your normal activities.
What Are the Benefits and Risks?
Benefits:
- CT scanning is painless, non-invasive, and accurate.
- One of the main advantages of CT is its ability to simultaneously image bone, soft tissue, and blood vessels.
- Unlike conventional X-rays, CT provides very detailed images of many types of tissues, including the lungs, bones, and blood vessels.
- CT scans are quick and simple; in emergency cases, they can reveal internal injuries and bleeding fast enough to help save lives.
- CT has been shown to be a cost-effective imaging tool for a wide range of clinical problems.
- CT is less sensitive to patient movement than MRI.
- Unlike MRI, CT can be performed if you have any implanted medical devices.
- CT provides real-time imaging; it is an excellent tool for guiding needle biopsies and minimally invasive procedures.
- A diagnosis made by a CT scan can eliminate the need for exploratory surgery and surgical biopsy.
- No radiation remains in a patient’s body after a CT examination.
Risks:
There is no definitive evidence that the small amounts of radiation used in CT scans cause cancer. When your doctor recommends a CT scan, the expected benefit of the test far outweighs the potential risk from radiation.
- Women should always inform their doctor or CT technician if there is any chance they are pregnant.
- In general, CT scans are not recommended for pregnant women unless medically necessary due to the potential risk to the fetus.
- Because children are more sensitive to radiation, CT should only be performed if it is essential for diagnosis, and repeat CT scans should be avoided unless absolutely necessary. CT scans for children should always use low-dose techniques.
Computed Tomography Prices 2026
To inquire about computed tomography prices, you can call us at 02126321059.